Ningbo Sunyer Machinery Co., Ltd.
METAL PRODUCTS

CATEGORY
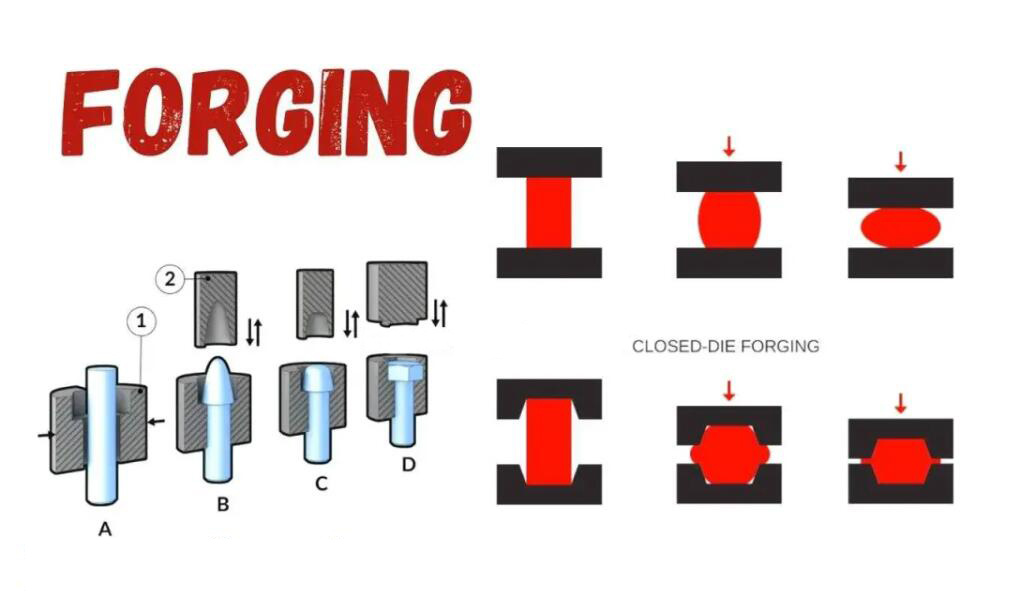
FORGING
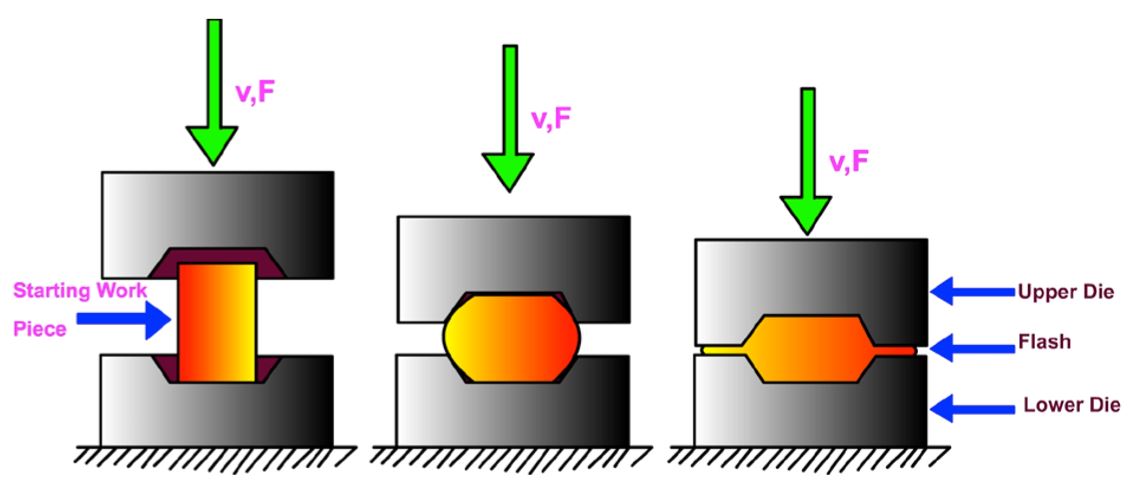
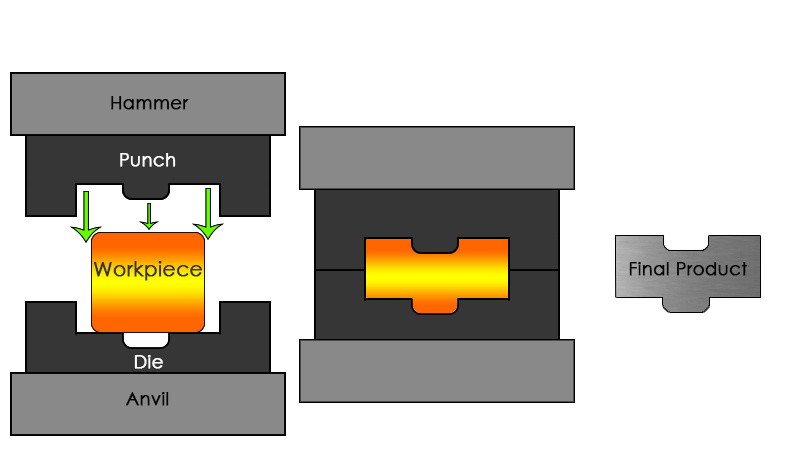
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forgings are often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging (a type of cold working), warm forging, or hot forging (a type of hot working). For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons. Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, cymbals, and jewellery. Since the Industrial Revolution, forged parts are widely used in mechanisms and machines wherever a component requires high strength; such forgings usually require further processing (such as machining) to achieve a finished part. Today, forging is a major worldwide industry.
ADVANTAGES OF FORGING
- High strength
- Low production cost
- High reliability and less prone to failure
- Suitable for further heat-treatment
- Versatility production capabilities
- High material flexibility
- Better mechanical properties than Casting or CNC machined parts
Application Of Forging
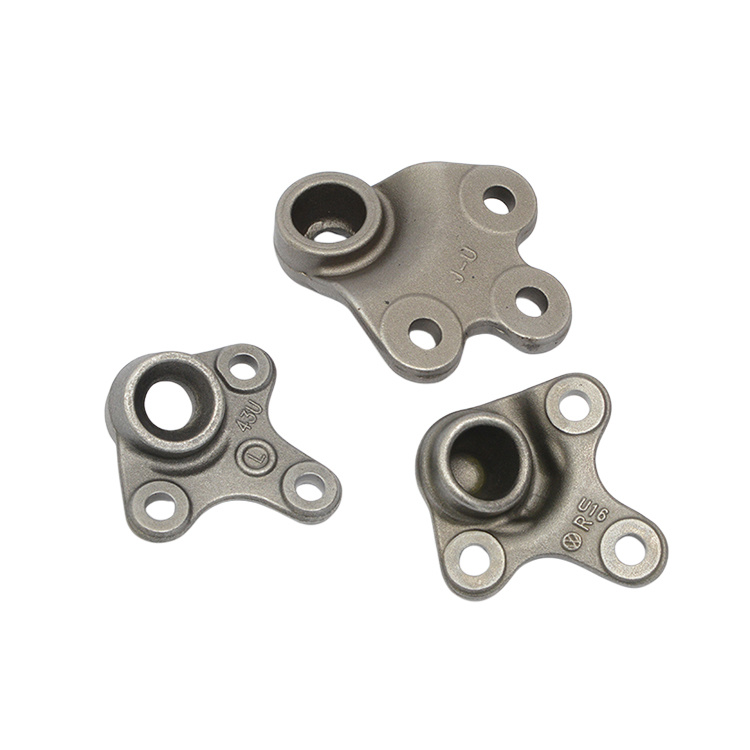
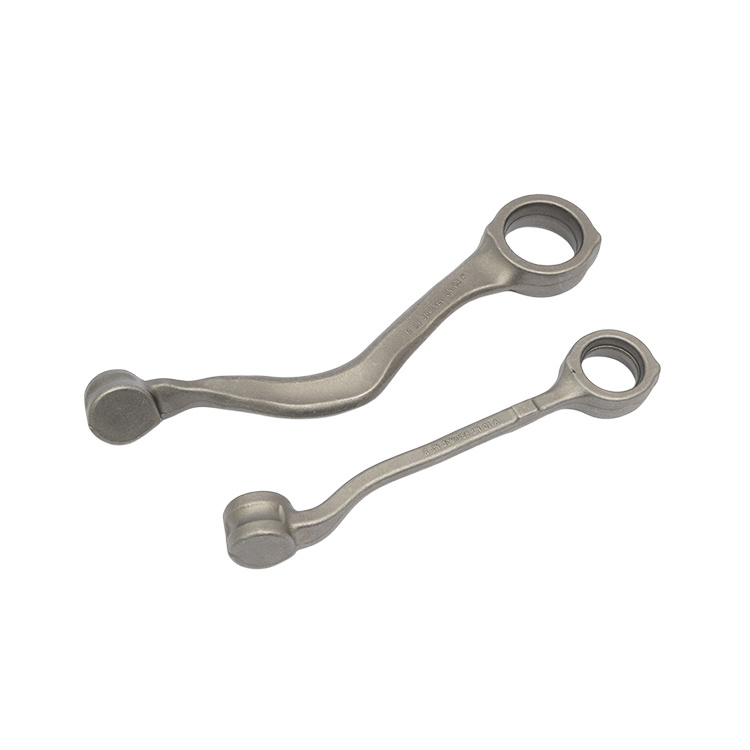
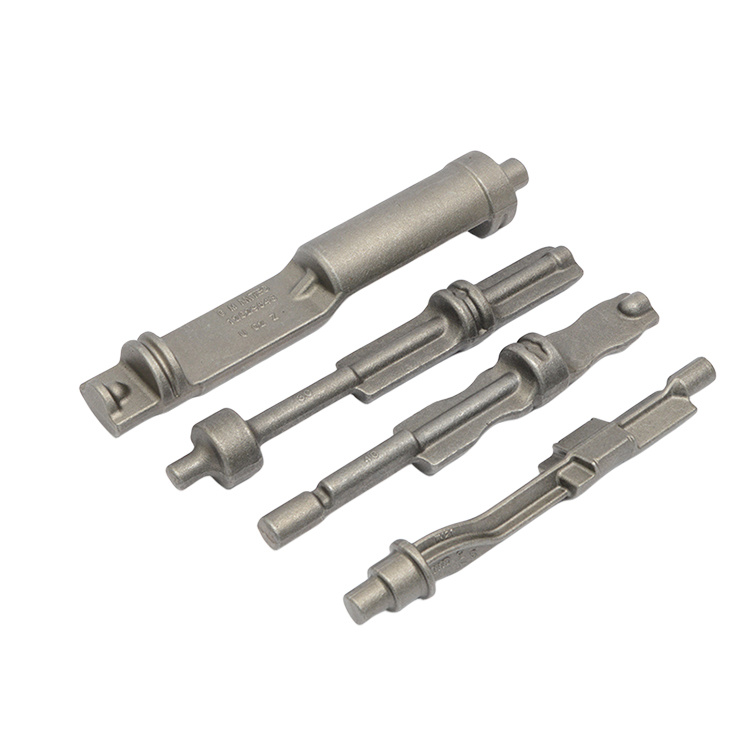
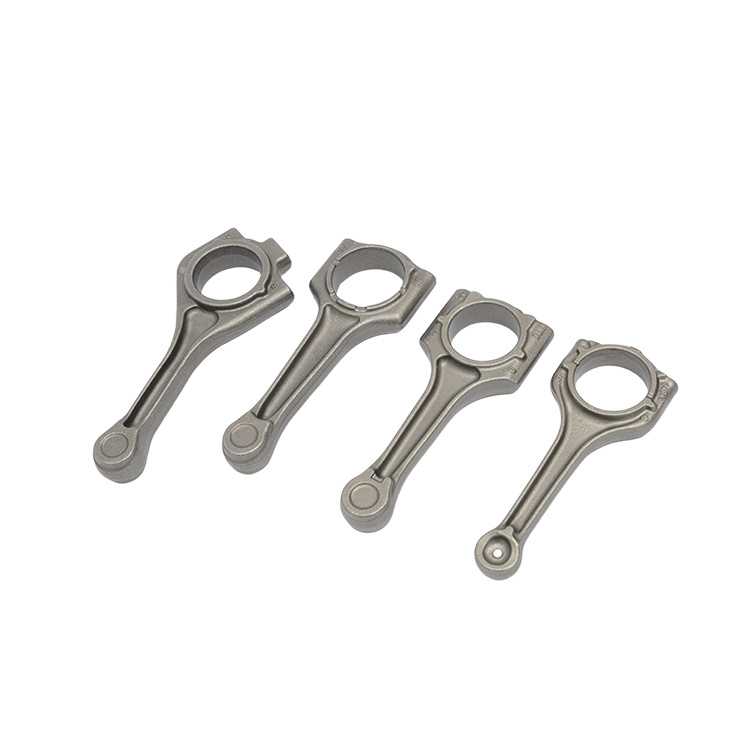
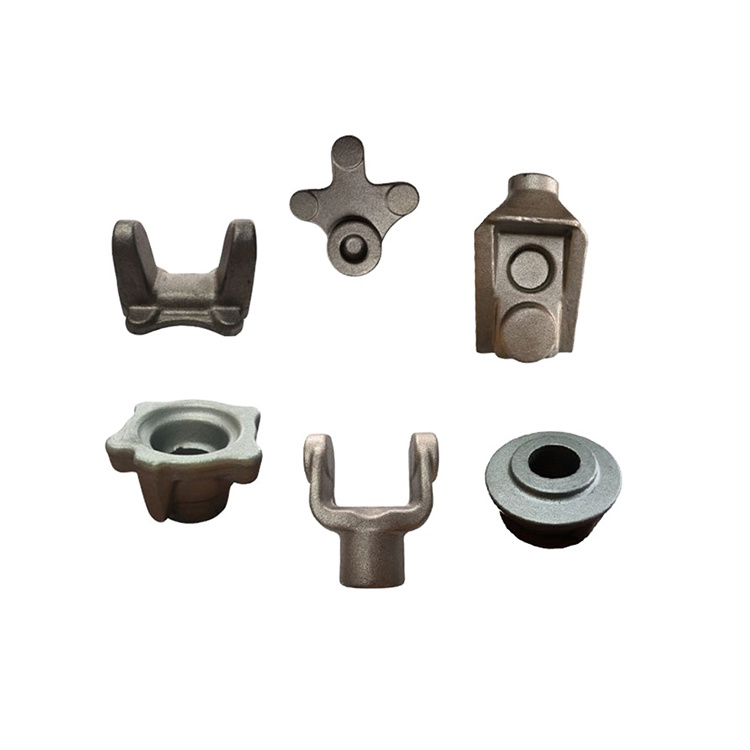
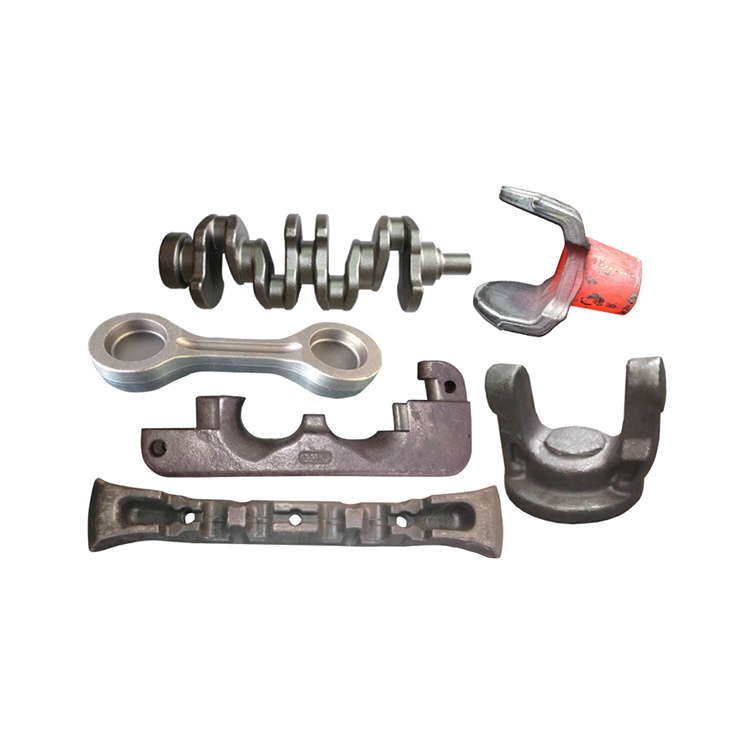
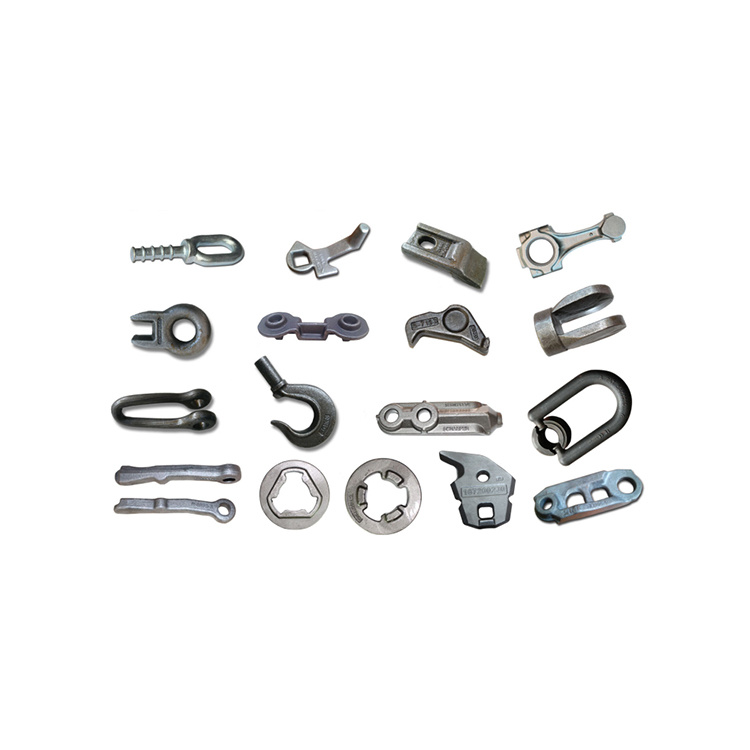
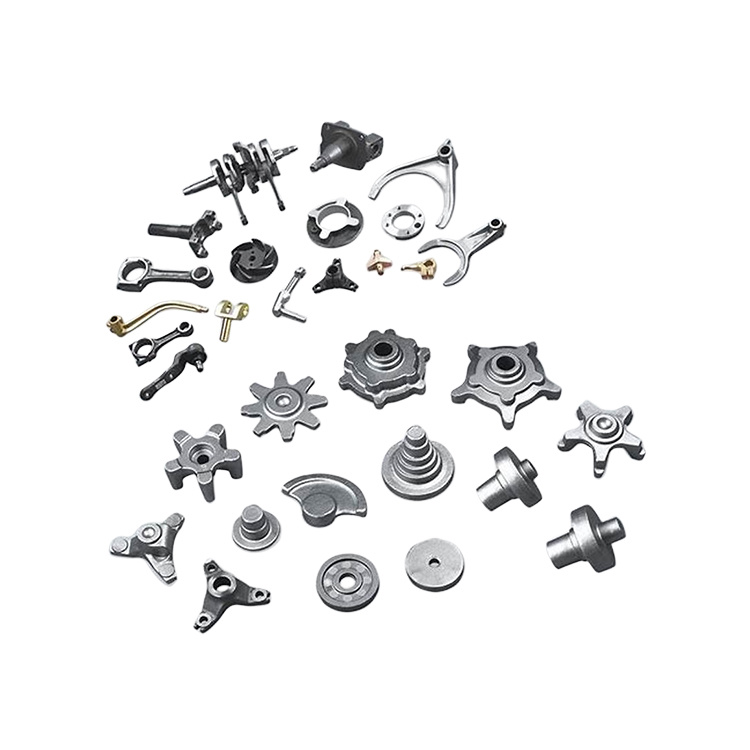
In addition to engine and transmission parts, forgings are used for a wide variety of gears, sprockets, levers, shafts, spindles, ball joints, wheel hubs, rollers, yokes, axle beams, bearing holders, and links.
- Mainly forged products are used in every mechanical industry.
- Turbine rotor, generator rotor etc. are forged product.
- It gives higher fatigue strength so most of moving parts like crankshaft, camshaft gears etc. are made by forging operation.
- Cold forging is used to produce chisel, bolts etc.
- These are mostly used in hand tools and hardware manufacturing.
- It is used in ship building in various structure works.
Advantages Of Forging
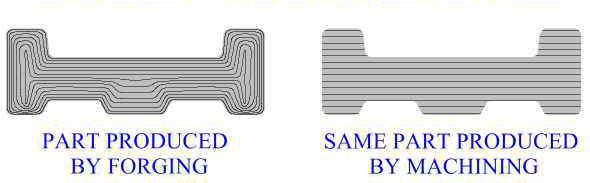
Forging provides better mechanical properties, ductility and fatigue, and impact resistance because this process refines and directs the grain flow according to the shape of the piece. Almost all metals, ferrous and non-ferrous can be forged.
- Parts manufactured by forging are stronger
- It is more reliable and less costly
- It offers better response to heat treatment
- It offers more consistent and better metallurgical properties
- It offers broad size range of products
- It requires fewer secondary operations
- It has great design flexibility
Disadvantages Of Forging
- In hot forging it is difficult to perform secondary operations
- Capital cost is more
- Very high man and material safety procedures need to be followed
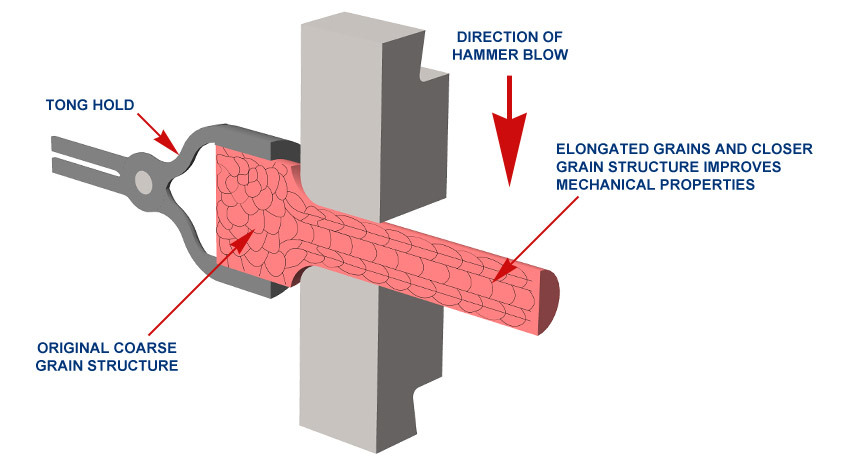
GRAIN STRUCTURE OF A FORGED PART COMPARED WITH A MACHINED PART