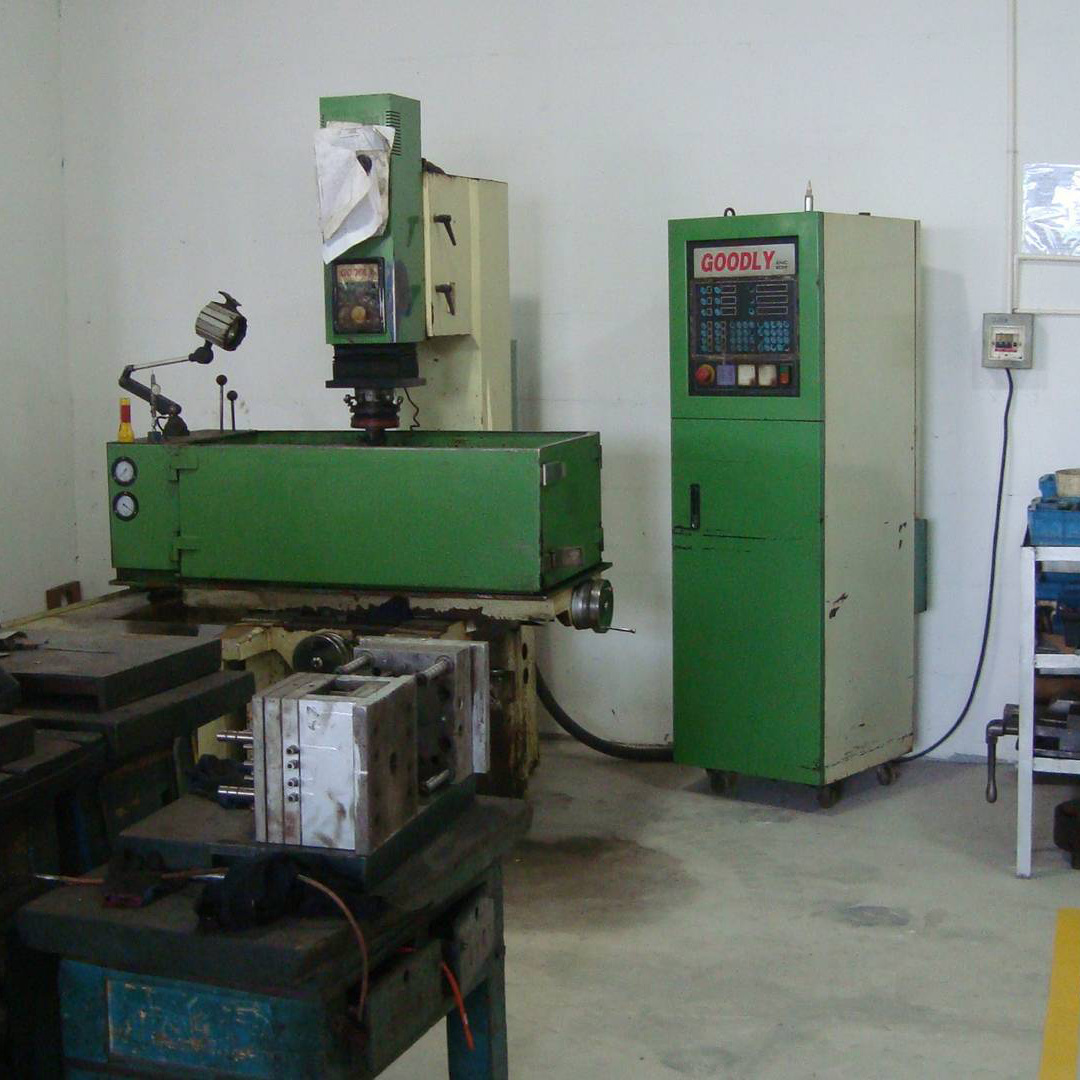
Ningbo Sunyer Machinery Co., Ltd.
INJECTION PLASTIC

CATEGORY
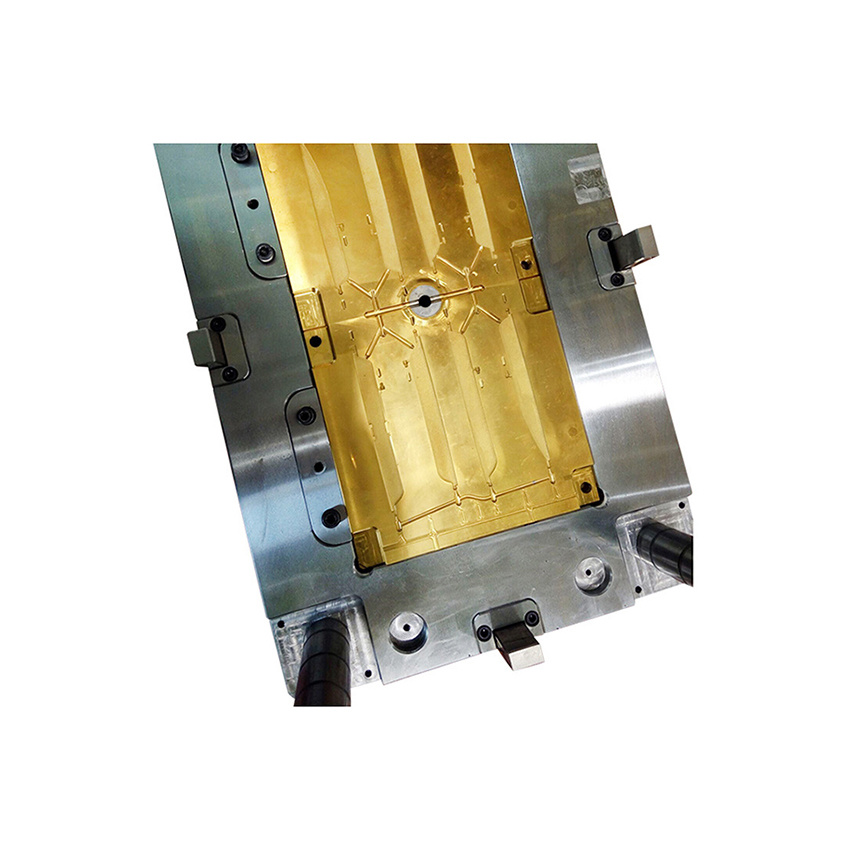
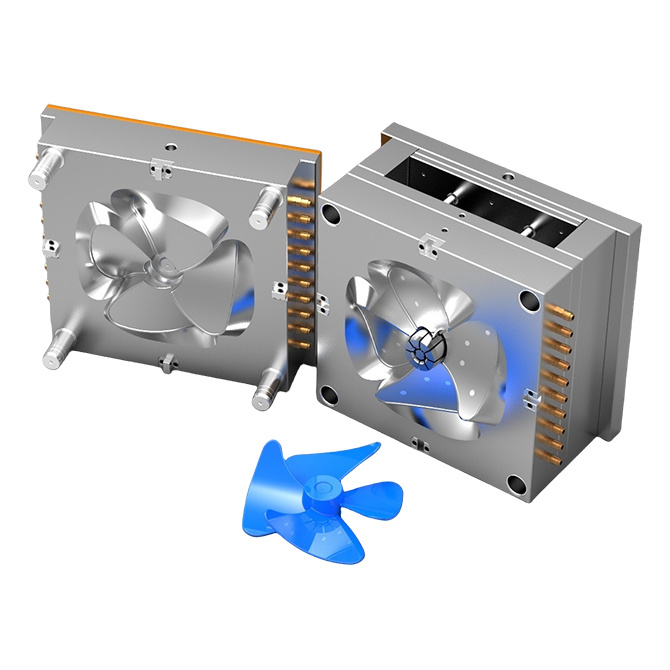
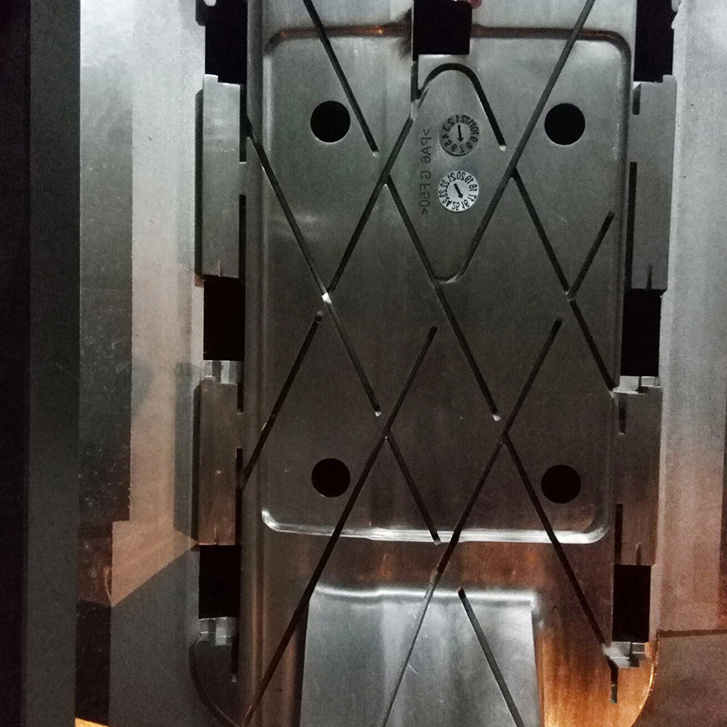
PLASTIC MOULDS
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
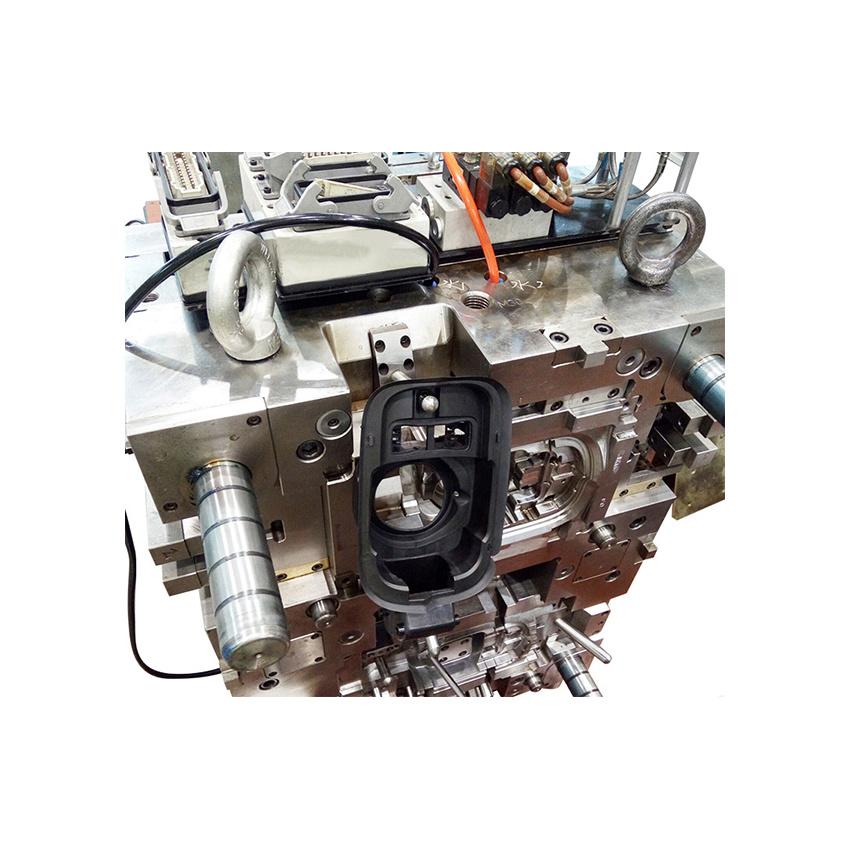
To create plastic parts, manufacturers use a process called plastic injection molding. Plastic injection molding involves injecting molten plastic into a mold to form the product. The plastic then cools in the shape of the product, creating the final product. In this processing, the temperature and pressure controlling are very important, and they will effect the quality of the final plastic product.
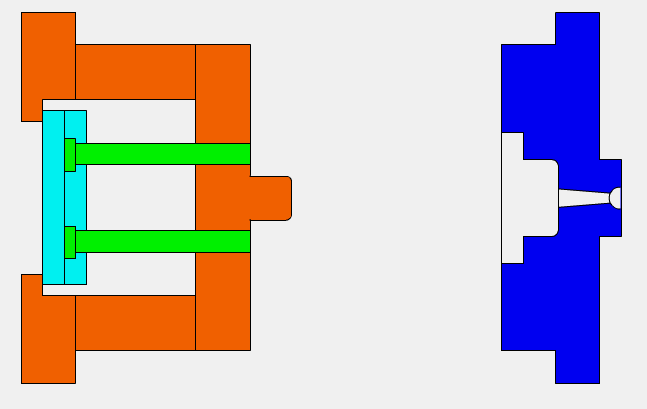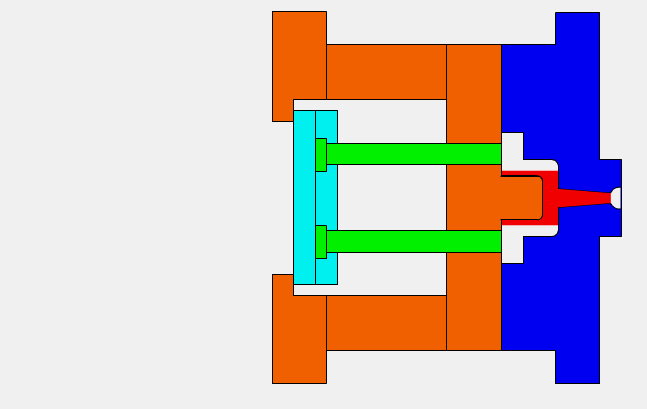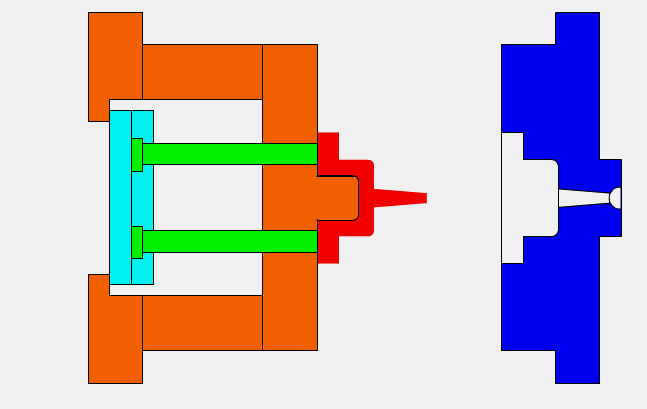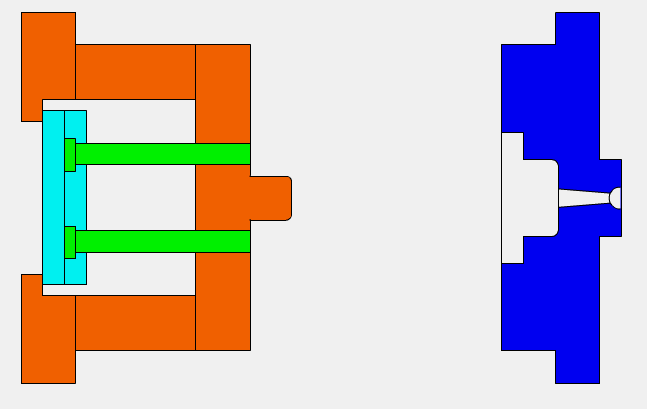
The Injection Molding Process

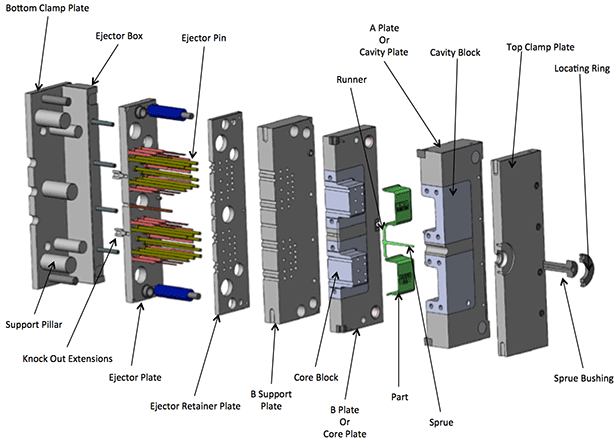
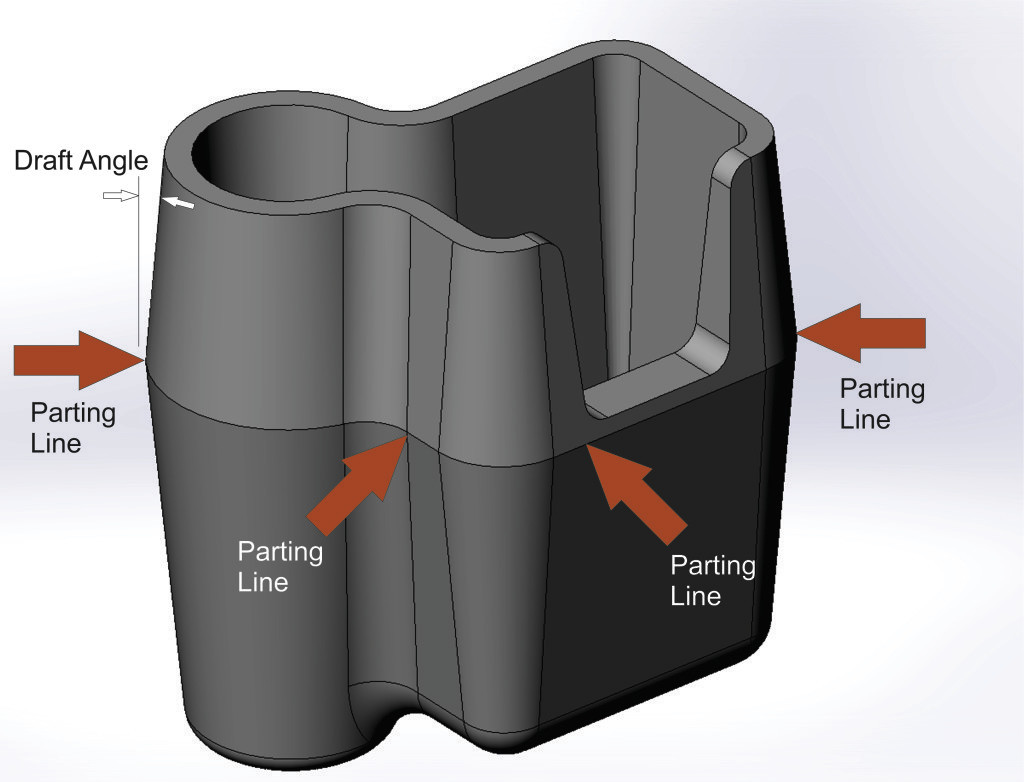
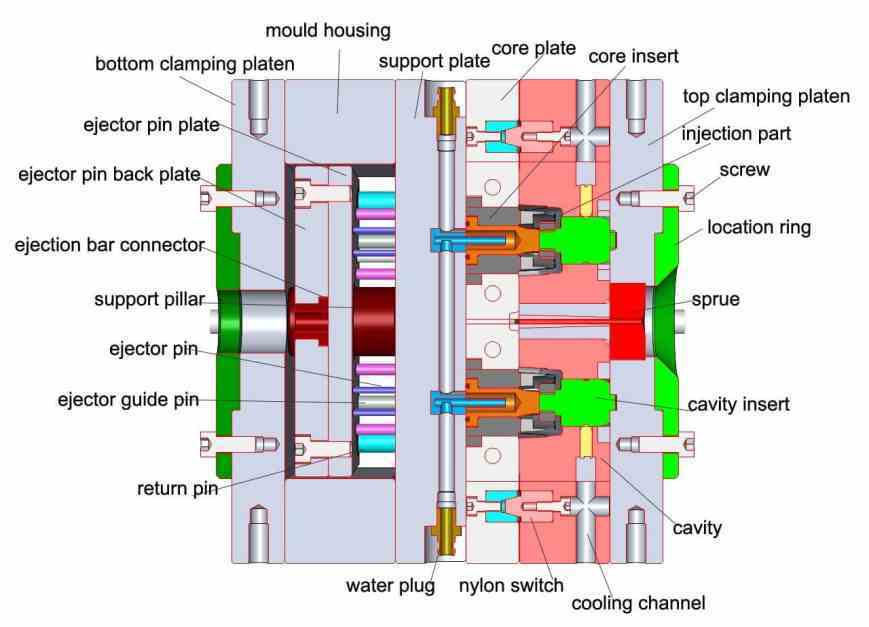
Step 1: A molding in the shape of the product is produced and split into two halves.
Step 2: At the beginning of the manufacturing process, the two halves of the mold are clamped together tightly by the molding machine.
Step 3: Plastic pellets are loaded into the machine via a hopper, which then travel through a heater and are melted down into molten plastic.
Step 4: The molten plastic is injected into the mold so that it completely fills it, before being cooled and turned into a solid form.
Step 5: The two clamps are separated, with the finished product then being ejected from the molding machine.
Types of Plastic Material for Injection Molding
It’s easy to get confused by the many types of plastic for injection molding that exist. There are many options for what to use in a plastic product, but by becoming familiar with the types of plastic you can ensure you are using what is best for the job.
Acrylic (PMMA)
Acrylic is a lightweight, shatter-resistant plastic also known as plexiglass. Since it is transparent and can withstand weathering effects like sunlight, heat, and rain, manufacturers often use acrylic as an alternative to glass. However, it is not good for bearing too much weight. Also, grease or oils can stain acrylic easily. Acrylic is mostly in windows, display cases, solar panels, light fixtures, and other clear applications.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, or ABS, is one of the more tough, inexpensive types of plastic. It resists impact, scratching and staining, but does not do well under sunlight or weathering. Due to this it is often seen in products like computer keyboards, plastic toys, wall socket covering plates, and interior car parts.
Nylon Polyamide (PA)
Nylon is a polyamide that offers very high resistance to friction, abrasion and heat. This makes it ideal for mechanical applications such as gears, bushings and bearings, and other parts that see a lot of movement and friction. However, it does not do well with water. It also isn’t naturally flame-resistant but can be made fire retardant.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is another clear plastic like acrylic, but it is much stronger. It is stiffer, more durable, and can withstand a wider range of temperatures. This allows manufacturers to use PC in a variety of applications, such as eyewear lenses, greenhouses, vehicle headlight covers, medical devices, LED lights, and clear tubing. It is also a glass substitute like acrylic, and while it is tougher, it is more expensive.
Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is an extremely common type of the plastic, and its properties can vary based on a chosen density. It is used for things like food packaging and trash bags, though those applications are not likely injection molded. When it comes to injection molding, polyethylene is used to make things such as toys, housewares, and hard cases such as some toolkits and lunchboxes. It is a cheap and tough plastic with a wide range of options, but with less temperature resistance and can be harder to mold in intricate designs.
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Due to its crystalline structure, polyoxymethylene sports impressive rigidity and resistance to friction. This makes it ideal for many engineering applications such as gears, bushings, and pulley wheels. POM is also used to make parts for mechanical systems in cars, locks, and firearms, or for stiff parts such as knife handles or eyeglass frames. It resists water and oils, but not fire or UV light.
Polypropylene (PP)
Another very commonly used type of plastic, polypropylene has numerous applications. It is hard, but also keeps its shape well, and can even be folded many times without breaking. An example of this would be the plastic cap on a condiment bottle that folds open to access a pour spout. It is food-safe and heat-resistant, but not flame resistant. It also sees use in other items such as containers and packaging, tools, toys, or even textile fabric. PP is highly recyclable.
Polystyrene (PS)
When it comes to injection molding polystyrene, there are two types of plastic that are variants of this resin: high impact (HIPS), and general purpose (GPPS). GPPS is more brittle, and therefore can break more easily. Both are lightweight and inexpensive, and resist water as well as radiation. This is useful in medical equipment, since it is often sterilized with gamma rays. HIPS is also in products such as car panels, gasoline tanks, drinking cups and many consumer products such as computer housings. While GPPS is in disposable cups and utensils, rigid packaging, petri dishes and more. A variant of PS is also used to make styrofoam, but this is not injection molded. PS is flammable and degrades with UV light and some chemicals.
Thermoplastic Elastomer (TPE)
A close up of someone wearing red and white Nike shoes on concrete stairs
TPE is a blend of various hard and soft components to achieve a wide range of flexibility, and therefore has some shared properties of rubber. This includes its elasticity, which makes it useful in footwear, seals, tubes and valves. Some of these applications include medical products like catheters or breathing devices. While it usually returns to its original shape, it can wear out with continued use and begins to lose this property under high heat exposure. It is also more expensive compared to other types of plastic.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)
TPU is actually a type of TPE, but is used so often that a distinction is made. When injection molded, it is much more durable than typical TPE, offering greater resistance to things like temperature, chemicals, abrasion, wear and tear. However, it is harder and less flexible, and more expensive. Manufacturers use TPU for product like phone cases, power tools, drive belts, and caster wheels.
Right here, we can create custom injection-molded parts out of whatever types of plastic are best for your product. Not only that, but we also offer mold making, prototyping, pad printing, 3D print, and many other services for startups and OEMs. Reach out to us for a free quote today!